Patient positioning is a improtent daily routine for a operation theater technologist , to access the surgical procedure . Different position is the cause of various physiological stress , nerve damage and pressure necrosis , the hypotension and hypothermia is also cause of these .
Diabetics patients with arterialdieases the elderly and those with neurological deficits are also at particular risk .
patient with rhematoid arthritis may suffer from survical spine instantly at the atlanto occipital lavel .
various types of positioning are -1 Supine position
2 Trendelenburg position,
3 Reverse Trendenburg position
4 PRONE POSITION
5 BACK CHAIR SITTING POSITION
6 LITHOTOMY POSITION
7 LATERAL POSITION
8 LAWN CHAIR POSITION
SUPINE POSITION - The supine or dorsal or decubitas is the position commonly used for this particularly surgery . Head is rested sand bag is used under the soulder . The patient arms are either tucked at their side and abducted to less than 90 degrees on padded arm boards . Acute flexicom elbow may cause ulnar nerve damage . Due to fixed structure brachial plexus is susceptible to traction injury . to avoid strech on the plexus pronate the foreman . when the arms is extended by the patient side . when the arms is extended by the patient side . When the arms is abducted head should be turned towards that side , again to prevent the brachial plexus . Legs should be turned towards that side , again to prevent the brachial plexus . Legs should be flat . A soft pad raising the heels form the table avoids pressure necrosis. this position for all common operation .Such as open gall bladder e.t.c .
 photo by google
photo by google
Trendelenburg position - It is a similar position with the supine position . But here the patients head is down and leg is up right position and the table is till towards the surgeon .
This particular position is used for LAPAROSCOPIC appendectomy surgery .

REVERSE TRENDELENBURG POSITION : Its also similar as trendelenburg position , but here head is up and leg is down and the table is till towards surgeon .
This particular position is used for LAPAROSCOPIC gall bllader and venicosa vein surgery .

Prone position : THIS position is particularly used for spinal surgery or back surgery . But this position is like as supine position but the patien should be truned down his face . the gab between patients hand and body is not more than 90 degrees but grater than 60 degrees .

Lateral position : Here the patient lay on the table on a side , one leg should be taken to the chest . And this position is used for kidney operation and hip joint operation and many other surgery .

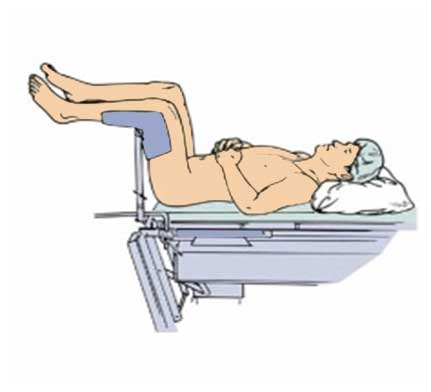
Lithotomy position :This position is frequently used on the operating table . This position is used for normal delivery , fissure , fistula and other surgery . legs should be up on the particular handle .
all of these position is used for different surgery on the operating table . and back chair position and lawn chair position is rear used for knee surgery .
HERE IS THE POSITION OF ALL TYPES OF SURGERIES .
Diabetics patients with arterialdieases the elderly and those with neurological deficits are also at particular risk .
patient with rhematoid arthritis may suffer from survical spine instantly at the atlanto occipital lavel .
various types of positioning are -1 Supine position
2 Trendelenburg position,
3 Reverse Trendenburg position
4 PRONE POSITION
5 BACK CHAIR SITTING POSITION
6 LITHOTOMY POSITION
7 LATERAL POSITION
8 LAWN CHAIR POSITION
| PATIENT POSITION ON OPERATING TABLE | PHOTO BY GOOGLE |
Trendelenburg position - It is a similar position with the supine position . But here the patients head is down and leg is up right position and the table is till towards the surgeon .
This particular position is used for LAPAROSCOPIC appendectomy surgery .

REVERSE TRENDELENBURG POSITION : Its also similar as trendelenburg position , but here head is up and leg is down and the table is till towards surgeon .
This particular position is used for LAPAROSCOPIC gall bllader and venicosa vein surgery .

Prone position : THIS position is particularly used for spinal surgery or back surgery . But this position is like as supine position but the patien should be truned down his face . the gab between patients hand and body is not more than 90 degrees but grater than 60 degrees .
Lateral position : Here the patient lay on the table on a side , one leg should be taken to the chest . And this position is used for kidney operation and hip joint operation and many other surgery .

Lithotomy position :This position is frequently used on the operating table . This position is used for normal delivery , fissure , fistula and other surgery . legs should be up on the particular handle .

all of these position is used for different surgery on the operating table . and back chair position and lawn chair position is rear used for knee surgery .
HERE IS THE POSITION OF ALL TYPES OF SURGERIES .
Comments
Post a Comment